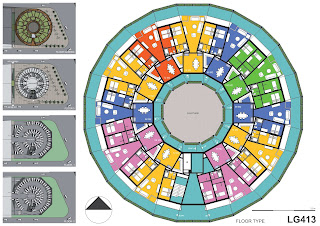
A cylindrical body, developed in spiral shape,
is incorporated into the environment as a green urban landmark reference.
Four interrelated subsystems conform the
building:
- The traffic and citizen
relationship at street level, with its square, commercial porches and
access to housing.
- The circulation and social
relationship of neighbors, with vertical access from the street (stairs
and elevators), communicating with the interior courtyard and the two
ramps, gardens on the sides (one indoor and one outdoor), culminating in
the green terrace. Instead of expanding the neighbors.
- The two-storey underground
garage with a parking space, at least one per housing (136).
- The residential units (132),
arranged so that the housing program can be one (58 m2), two (72 m2),
three (86 m2) or four bedrooms (100 m2).
The inner courtyard and ramp build up a space
that can be used as a meeting place (address issues of community or parties).
Outer ramp besides being a circulation space is
a place of encounter and relationship between neighbors.
The apartments have entrance, kitchen, living
room and a small outdoor area connected to the outer ramp and expanded with the
corresponding bedrooms and bathrooms.
Cross ventilation, each and every one of the
houses, are guaranteed by having two opposing vertical walls and ventilation conducts.
The entrance and exit of the garage through
ramps are available along the dividing of the adjoining property by attaching a
vertical green wall.
The roof cover allows installation of devices
for the use of solar and wind energy.
Cellular and tubular structure of laminated
timber (KLH type) floors of housing are developed on the basis of a reinforced
concrete structure of the basement and ground floor. The relationship ramps and
act as structural stiffeners.
Wooden constructions are energy efficient in
two respects: First because wood is a natural and renewable resource. Second,
wood has natural insulating qualities. So these qualities save energy in
heating and cooling the building.
There are advantages of laminated wood:
- A sustainable material from an ecological
point of view.
- It has a positive ecological balance.
- Getting healthy and pleasant indoor
environments.
- Solid wood construction is stable.
- It is compatible with reinforced concrete,
glass and other materials.
- It has excellent static properties.
- Prefabricated elements with high accuracy
measurements are obtained.
- Easy assembly.
- Reduced construction time.
- Dry construction.
- Quick availability of buildings for
habitation.